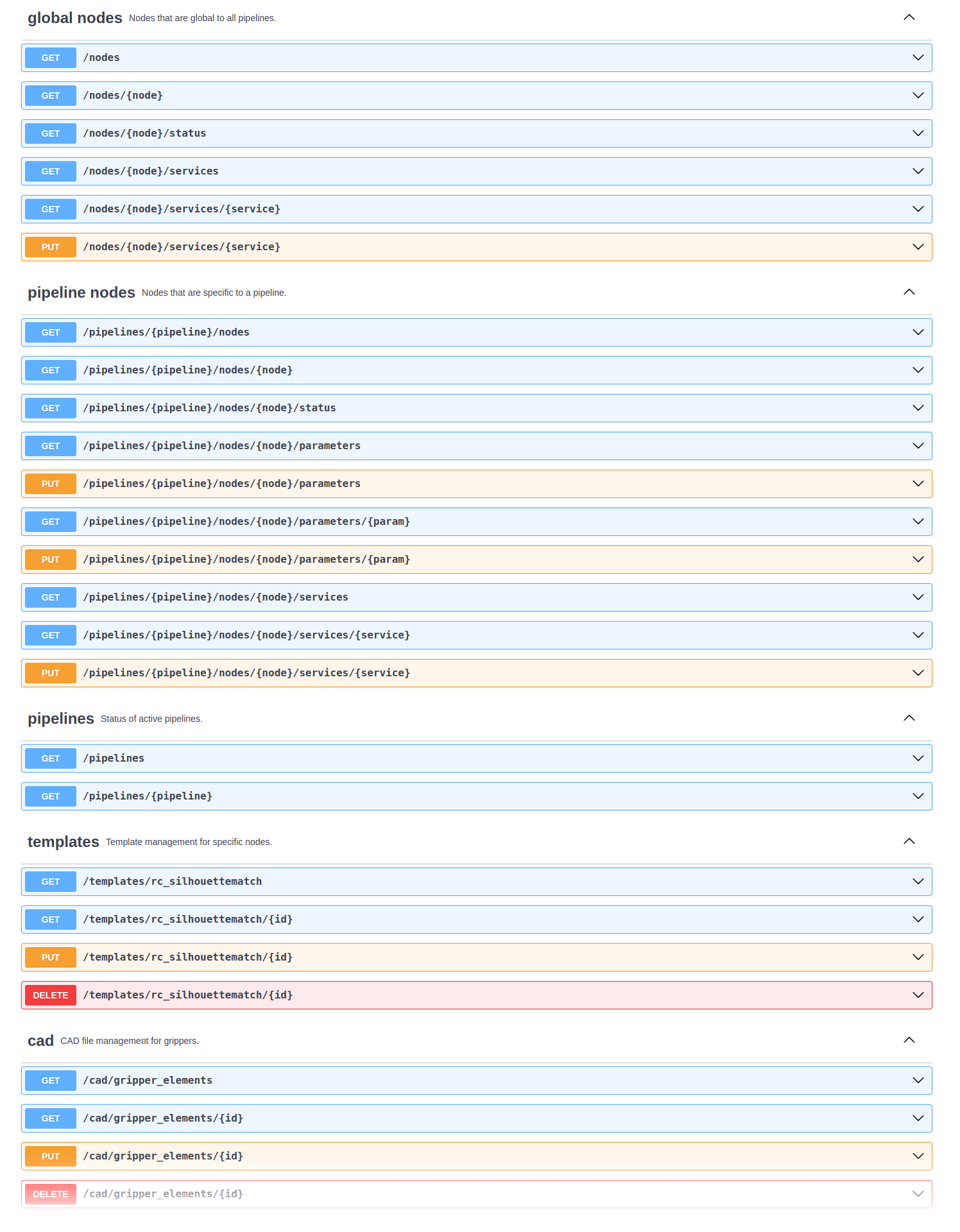
Swagger UI¶
The rc_visard NG’s Swagger UI allows developers to easily
visualize and interact with the REST-API, e.g., for development and testing. Accessing
http://<host>/api/ or http://<host>/api/swagger
(the former will automatically be redirected to the latter) opens a visualization
of the rc_visard NG’s general API structure including all
available resources and requests
and offers a simple user interface for exploring all of its features.
Note
Users must be aware that, although the rc_visard NG’s Swagger UI is
designed to explore and test the REST-API, it is a fully
functional interface.
That is, any issued requests are actually
processed and particularly PUT, POST, and DELETE
requests might change the overall status and/or behavior of the
device.
Using this interface, available resources and requests can be explored by
clicking on them to uncollapse or recollapse them.
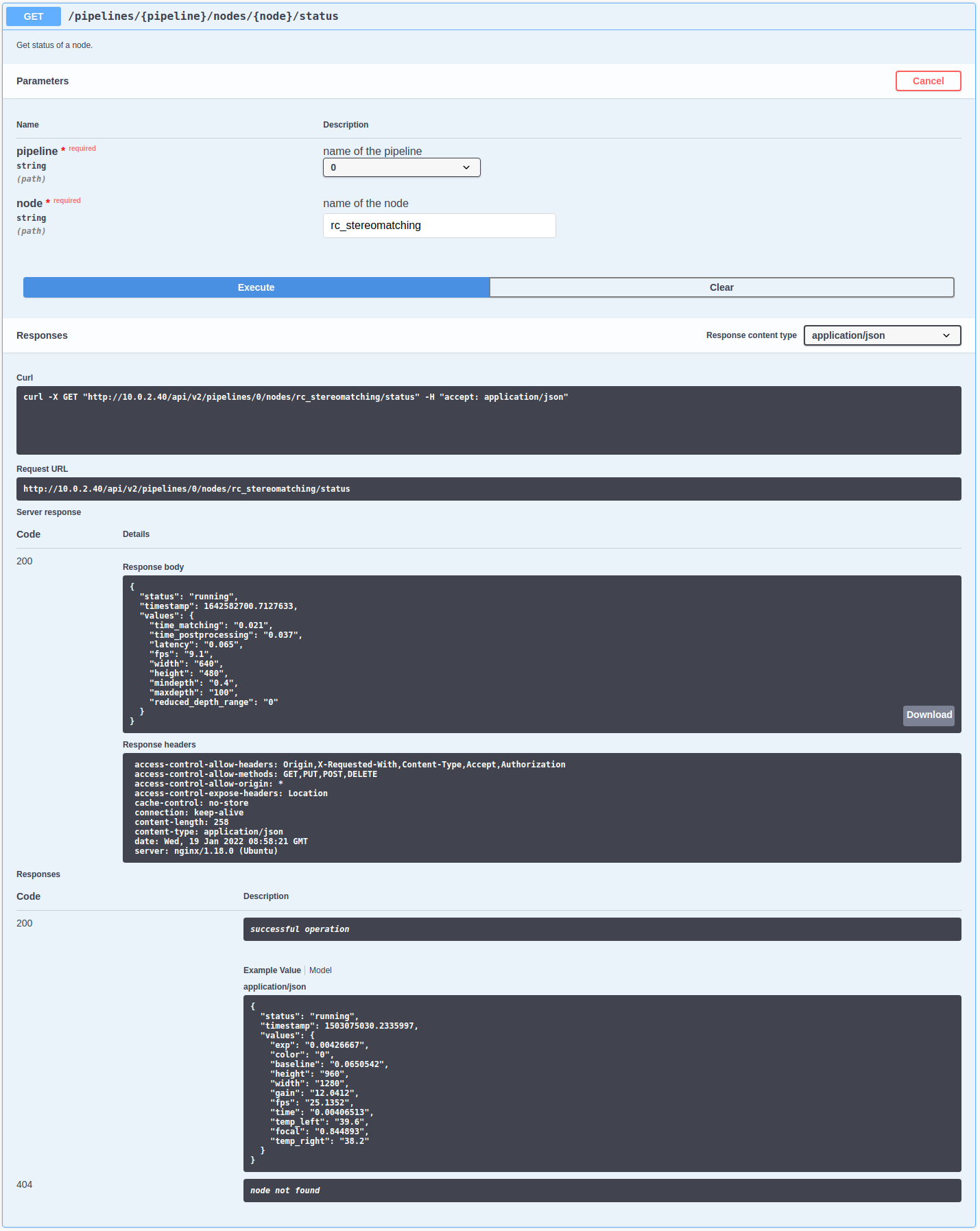
The following figure shows an example of how to get a node’s current status
by clicking the Try it out! button, filling in the necessary parameters
(pipeline number and node name) and clicking Execute. This action results in the Swagger UI showing,
amongst others, the actual curl command that was executed when
issuing the request as well as the response body showing the current status
of the requested node in a JSON-formatted string.
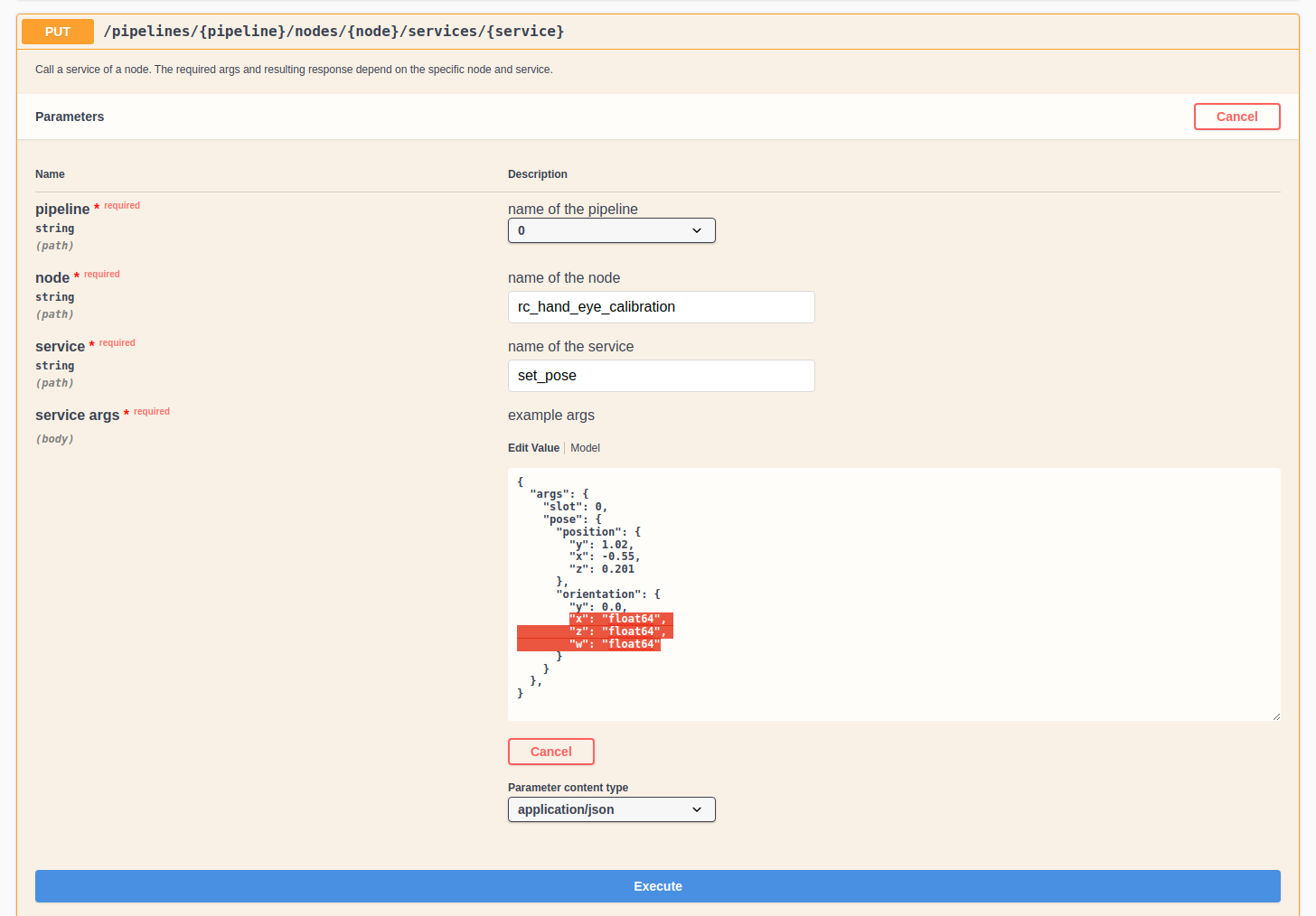
Some actions, such as setting parameters or calling services, require more
complex parameters to an HTTP request. The Swagger UI allows developers to
explore the attributes required for these actions during run-time, as shown in
the next example. In the figure below, the attributes required for the
the rc_hand_eye_calibration node’s set_pose service are explored by
performing a GET request on this resource. The response features a full
description of the service offered, including all required arguments with
their names and types as a JSON-formatted string.
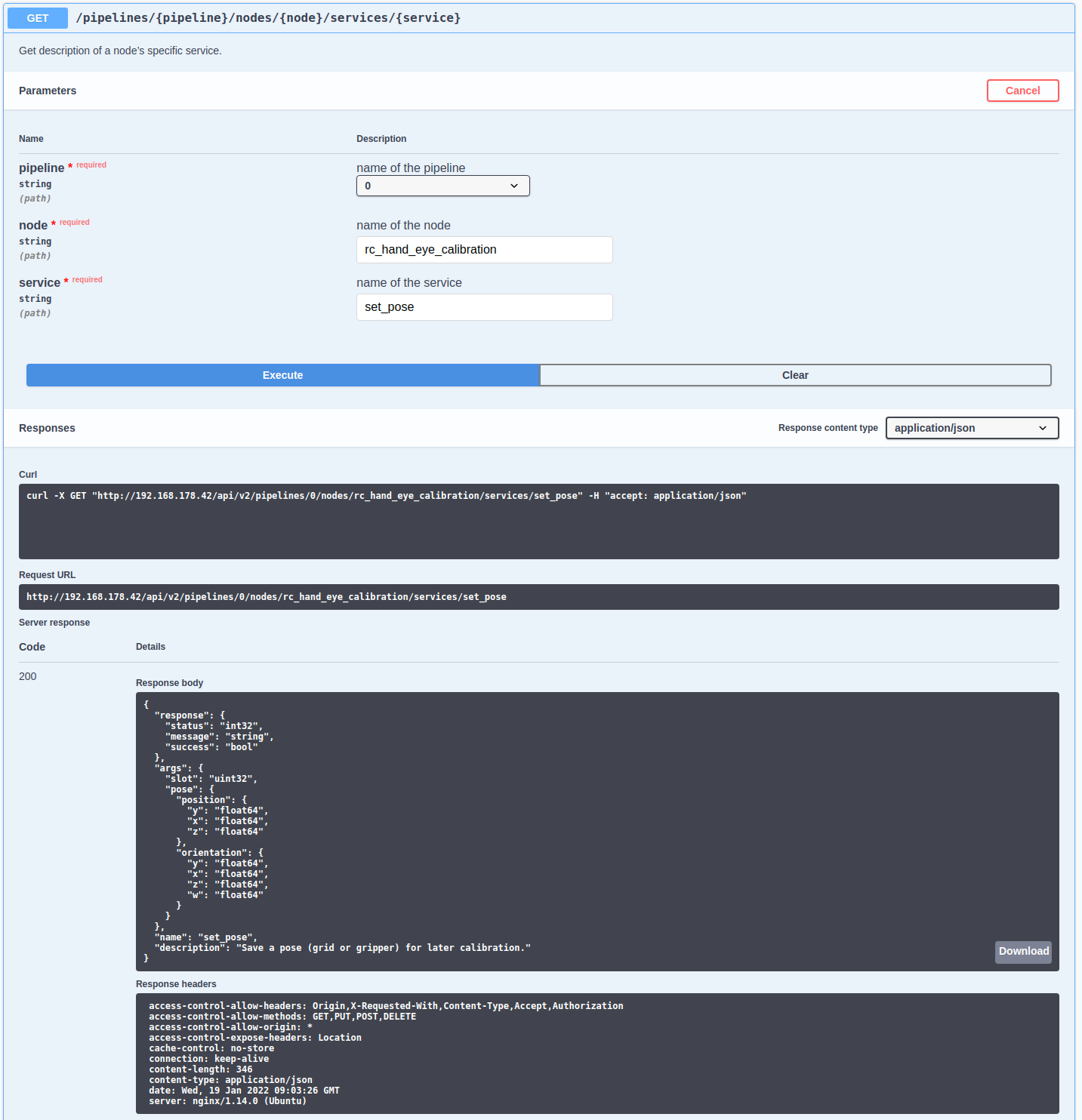
Fig. 60 The result of the GET request on the set_pose service shows the
required arguments for this service call.
Users can easily use this preformatted JSON string as a template for the service arguments to actually call the service: